|
Palomar 12
Palomar 12 is a globular cluster in the constellation Capricornus, and is a member of the Palomar Globular Clusters group. First discovered on the National Geographic Society – Palomar Observatory Sky Survey plates by Robert George Harrington and Fritz Zwicky, it was initially catalogued as a globular cluster; however, Zwicky came to believe it was actually a nearby dwarf galaxy in the Local Group. It is a relatively young cluster, being about 30% younger than most of the globular clusters in the Milky Way. It is metal-rich with a metallicity of . It has an average luminosity distribution of . Based on proper motion studies, this cluster was first suspected in 2000 to have been captured from the Sagittarius Dwarf Elliptical Galaxy (''SagDEG'') about 1.7 Ga ago. It is now generally believed to have originated in that galaxy and is associated with the Sagittarius Stream. It is estimated to be 6.5 Gyr old. See also *Messier 54 References External links Simbad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hubble Space Telescope
The Hubble Space Telescope (often referred to as HST or Hubble) is a space telescope that was launched into low Earth orbit in 1990 and remains in operation. It was not the first space telescope, but it is one of the largest and most versatile, renowned both as a vital research tool and as a public relations boon for astronomy. The Hubble telescope is named after astronomer Edwin Hubble and is one of NASA's Great Observatories. The Space Telescope Science Institute (STScI) selects Hubble's targets and processes the resulting data, while the Goddard Space Flight Center (GSFC) controls the spacecraft. Hubble features a mirror, and its five main instruments observe in the ultraviolet, visible, and near-infrared regions of the electromagnetic spectrum. Hubble's orbit outside the distortion of Earth's atmosphere allows it to capture extremely high-resolution images with substantially lower background light than ground-based telescopes. It has recorded some of the most detaile ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metallicity
In astronomy, metallicity is the abundance of elements present in an object that are heavier than hydrogen and helium. Most of the normal physical matter in the Universe is either hydrogen or helium, and astronomers use the word ''"metals"'' as a convenient short term for ''"all elements except hydrogen and helium"''. This word-use is distinct from the conventional chemical or physical definition of a metal as an electrically conducting solid. Stars and nebulae with relatively high abundances of heavier elements are called "metal-rich" in astrophysical terms, even though many of those elements are nonmetals in chemistry. The presence of heavier elements hails from stellar nucleosynthesis, where the majority of elements heavier than hydrogen and helium in the Universe (''metals'', hereafter) are formed in the cores of stars as they evolve. Over time, stellar winds and supernovae deposit the metals into the surrounding environment, enriching the interstellar medium and providing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Astronomical Objects Discovered In 1955
Astronomy () is a natural science that studies celestial objects and phenomena. It uses mathematics, physics, and chemistry in order to explain their origin and evolution. Objects of interest include planets, moons, stars, nebulae, galaxies, and comets. Relevant phenomena include supernova explosions, gamma ray bursts, quasars, blazars, pulsars, and cosmic microwave background radiation. More generally, astronomy studies everything that originates beyond Earth's atmosphere. Cosmology is a branch of astronomy that studies the universe as a whole. Astronomy is one of the oldest natural sciences. The early civilizations in recorded history made methodical observations of the night sky. These include the Babylonians, Greeks, Indians, Egyptians, Chinese, Maya, and many ancient indigenous peoples of the Americas. In the past, astronomy included disciplines as diverse as astrometry, celestial navigation, observational astronomy, and the making of calendars. Nowadays, professional a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sagittarius Dwarf Spheroidal Galaxy
The Sagittarius Dwarf Spheroidal Galaxy (Sgr dSph), also known as the Sagittarius Dwarf Elliptical Galaxy (Sgr dE or Sag DEG), is an elliptical loop-shaped satellite galaxy of the Milky Way. It contains four globular clusters in its main body, with the brightest of them – NGC 6715 (M54) – being known well before the discovery of the galaxy itself in 1994. Sgr dSph is roughly 10,000 light-years in diameter, and is currently about 70,000 light-years from Earth, travelling in a polar orbit (an orbit passing over the Milky Way's galactic poles) at a distance of about 50,000 light-years from the core of the Milky Way (about one third of the distance of the Large Magellanic Cloud). In its looping, spiraling path, it has passed through the plane of the Milky Way several times in the past. In 2018 the Gaia project of the European Space Agency showed that Sgr dSph had caused perturbations in a set of stars near the Milky Way's core, causing unexp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Globular Clusters
A globular cluster is a spheroidal conglomeration of stars. Globular clusters are bound together by gravity, with a higher concentration of stars towards their centers. They can contain anywhere from tens of thousands to many millions of member stars. Their name is derived from Latin (small sphere). Globular clusters are occasionally known simply as "globulars". Although one globular cluster, Omega Centauri, was observed in antiquity and long thought to be a star, recognition of the clusters' true nature came with the advent of telescopes in the 17th century. In early telescopic observations globular clusters appeared as fuzzy blobs, leading French astronomer Charles Messier to include many of them in his catalog of astronomical objects that he thought could be mistaken for comets. Using larger telescopes, 18th-century astronomers recognized that globular clusters are groups of many individual stars. Early in the 20th century the distribution of globular clusters in the sky wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
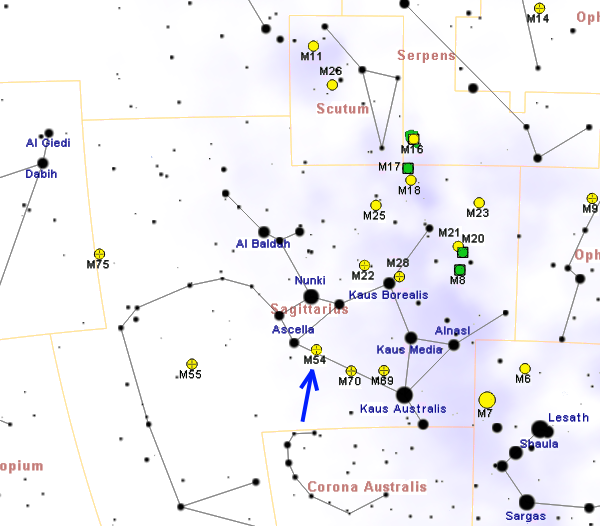
Messier 54
Messier 54 (also known as M54 or NGC 6715) is a globular cluster in the constellation Sagittarius. It was discovered by Charles Messier in 1778 and then included in his catalog of comet-like objects. It is easily found in the sky, being close to the star ζ Sagittarii. It is, however, not resolvable into individual stars even with larger amateur telescopes. In July 2009, a team of astronomers reported that they had found evidence of an intermediate-mass black hole in the core of M54. Distance Previously thought to belong to the Milky Way at a distance from Earth of about 50,000 light-years, it was discovered in 1994 that M54 most likely belongs to the Sagittarius Dwarf Elliptical Galaxy (''SagDEG''), making it the first globular cluster formerly thought to be part of our galaxy reassigned to extragalactic status, even if not recognized as such for nearly two and a quarter centuries. As it is located in SagDEG's center, some authors think it actually may be its core; howev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sagittarius Stream
In astronomy, the Sagittarius Stream is a long, complex structure made of stars that wrap around the Milky Way galaxy in an orbit that nearly crosses the galactic poles. It consists of Tidal stripping, tidally stripped stars from the Sagittarius Dwarf Elliptical Galaxy, resulting from the process of Galaxy merger, merging with the Milky Way over a period of billions of years. This stellar stream was originally proposed in 1995 by Donald Lynden-Bell after analyzing the distribution of globular clusters in the Milky Way. The actual structure was identified by Newberg and associates (2002) plus Majewski and associates (2003) using data from the 2MASS and Sloan Digital Sky Survey, SDSS surveys. In 2006, Belokurov and his collaborators found that the Sagittarius Stream has two branches. When the progenitor object was shredded apart during the interaction, it sent oscillations (analogous to sound waves) through the Milky Way spiral arm structure. The effects of the oscillations are obser ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gigaannum
A year or annus is the orbital period of a planetary body, for example, the Earth, moving in its orbit around the Sun. Due to the Earth's axial tilt, the course of a year sees the passing of the seasons, marked by change in weather, the hours of daylight, and, consequently, vegetation and soil fertility. In temperate and subpolar regions around the planet, four seasons are generally recognized: spring, summer, autumn and winter. In tropical and subtropical regions, several geographical sectors do not present defined seasons; but in the seasonal tropics, the annual wet and dry seasons are recognized and tracked. A calendar year is an approximation of the number of days of the Earth's orbital period, as counted in a given calendar. The Gregorian calendar, or modern calendar, presents its calendar year to be either a common year of 365 days or a leap year of 366 days, as do the Julian calendars. For the Gregorian calendar, the average length of the calendar year (the mean y ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sagittarius Dwarf Elliptical Galaxy
The Sagittarius Dwarf Spheroidal Galaxy (Sgr dSph), also known as the Sagittarius Dwarf Elliptical Galaxy (Sgr dE or Sag DEG), is an elliptical loop-shaped satellite galaxy of the Milky Way. It contains four globular clusters in its main body, with the brightest of them – NGC 6715 (M54) – being known well before the discovery of the galaxy itself in 1994. Sgr dSph is roughly 10,000 light-years in diameter, and is currently about 70,000 light-years from Earth, travelling in a polar orbit (an orbit passing over the Milky Way's galactic poles) at a distance of about 50,000 light-years from the core of the Milky Way (about one third of the distance of the Large Magellanic Cloud). In its looping, spiraling path, it has passed through the plane of the Milky Way several times in the past. In 2018 the Gaia project of the European Space Agency showed that Sgr dSph had caused perturbations in a set of stars near the Milky Way's core, causing unexp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proper Motion
Proper motion is the astrometric measure of the observed changes in the apparent places of stars or other celestial objects in the sky, as seen from the center of mass of the Solar System, compared to the abstract background of the more distant stars. The components for proper motion in the equatorial coordinate system (of a given epoch, often J2000.0) are given in the direction of right ascension (''μ''α) and of declination (''μ''δ). Their combined value is computed as the ''total proper motion'' (''μ''). It has dimensions of angle per time, typically arcseconds per year or milliarcseconds per year. Knowledge of the proper motion, distance, and radial velocity allows calculations of an object's motion from our star system's frame of reference and its motion from the galactic frame of reference – that is motion in respect to the Sun, and by coordinate transformation, that in respect to the Milky Way. Introduction Over the course of centuries, stars appear t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Milky Way
The Milky Way is the galaxy that includes our Solar System, with the name describing the galaxy's appearance from Earth: a hazy band of light seen in the night sky formed from stars that cannot be individually distinguished by the naked eye. The term ''Milky Way'' is a translation of the Latin ', from the Greek ('), meaning "milky circle". From Earth, the Milky Way appears as a band because its disk-shaped structure is viewed from within. Galileo Galilei first resolved the band of light into individual stars with his telescope in 1610. Until the early 1920s, most astronomers thought that the Milky Way contained all the stars in the Universe. Following the 1920 Great Debate between the astronomers Harlow Shapley and Heber Curtis, observations by Edwin Hubble showed that the Milky Way is just one of many galaxies. The Milky Way is a barred spiral galaxy with an estimated D25 isophotal diameter of , but only about 1,000 light years thick at the spiral arms (more at the bulg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epoch (astronomy)
In astronomy, an epoch or reference epoch is a moment in time used as a reference point for some time-varying astronomical quantity. It is useful for the celestial coordinates or orbital elements of a celestial body, as they are subject to perturbations and vary with time. These time-varying astronomical quantities might include, for example, the mean longitude or mean anomaly of a body, the node of its orbit relative to a reference plane, the direction of the apogee or aphelion of its orbit, or the size of the major axis of its orbit. The main use of astronomical quantities specified in this way is to calculate other relevant parameters of motion, in order to predict future positions and velocities. The applied tools of the disciplines of celestial mechanics or its subfield orbital mechanics (for predicting orbital paths and positions for bodies in motion under the gravitational effects of other bodies) can be used to generate an ephemeris, a table of values giving the posit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |